Hand powered Survival Device
(ME Design Project)
Key Design Requirements
- Cost target: Less than $20 per unit for manufacturability and scalability
- Form factor: Compact handheld design (~160 × 50 × 135 mm, <3 lb)
- Ergonomics: Designed to fit 6.3–8.1 in hand sizes with non-slip grip
- Power generation: 2–3.5 W output at ≤12 V using a brushless DC motor
- Energy storage: 1000 mAh onboard storage
- Mechanical transmission: 62:1 gearbox designed for ≥10,000 cycles
- Reliability: Stainless steel gearing to reduce wear and corrosion
Design Process
-
Role
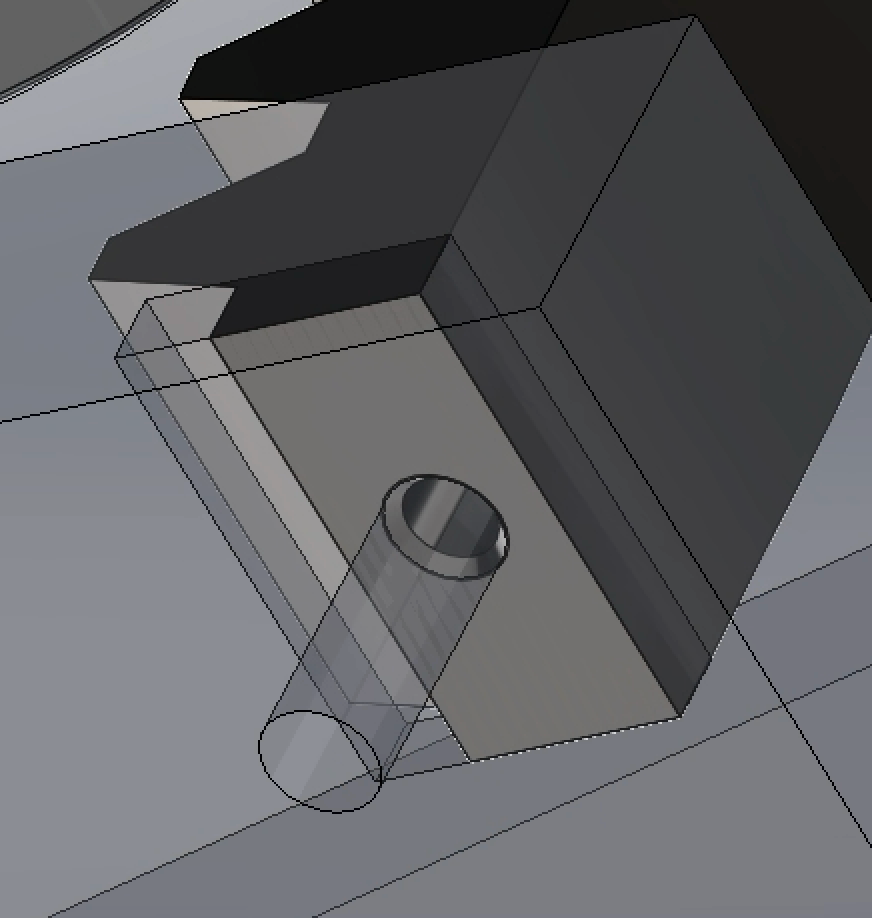
- Owned the design + verification of the curved gear rack, the primary element that transfers the handle squeeze force into the first drive gear and initiates motion in the gear system.
- Performed hand calculations and SolidWorks FEA checks to validate strength, stability, fatigue life, and gear-tooth performance; coordinated interface requirements with the curved rack screw and drive gear.
-
Component
-
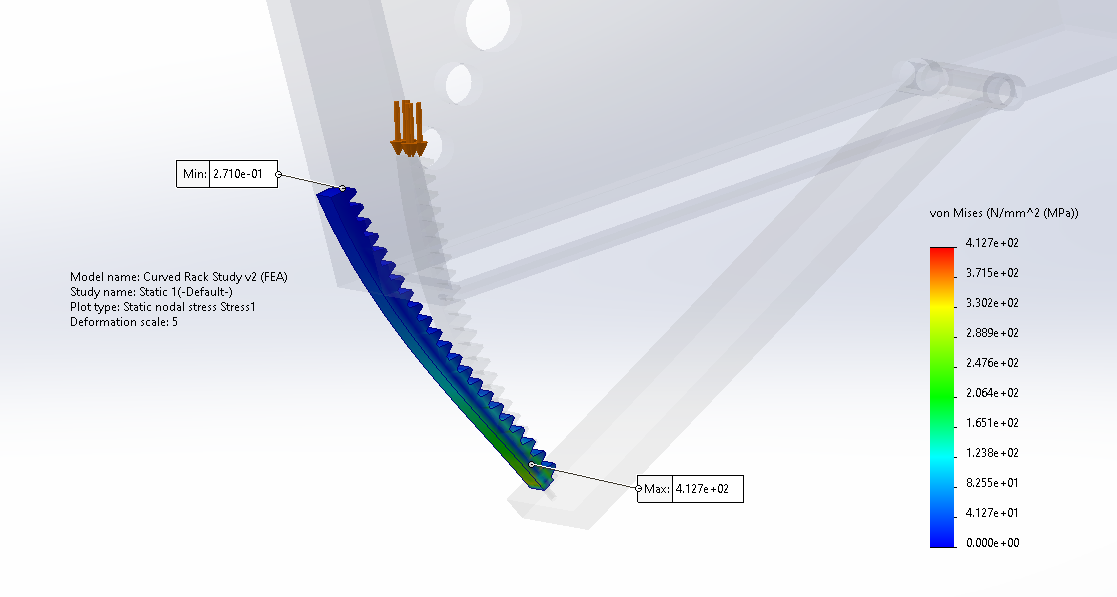
Static: Curved Gear Rack — FS = 1.65
- Verified bending-driven yielding risk at the fixed connection region under peak squeeze loading.
-
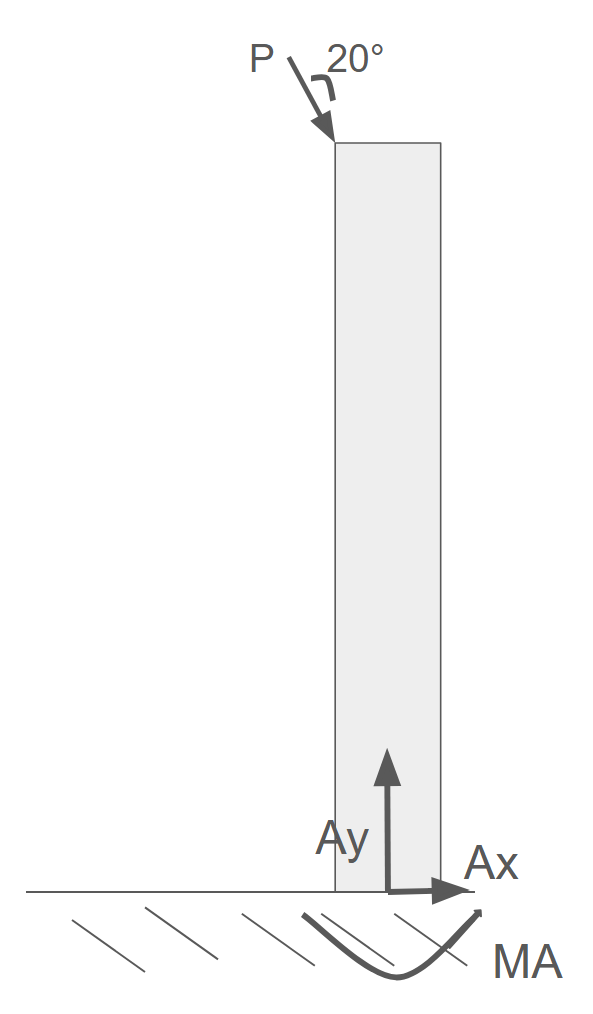
Buckling: Curved Gear Rack — FS = 26.42 (hand calc)
 ,
~4.74 (SolidWorks buckling FEA)
,
~4.74 (SolidWorks buckling FEA)
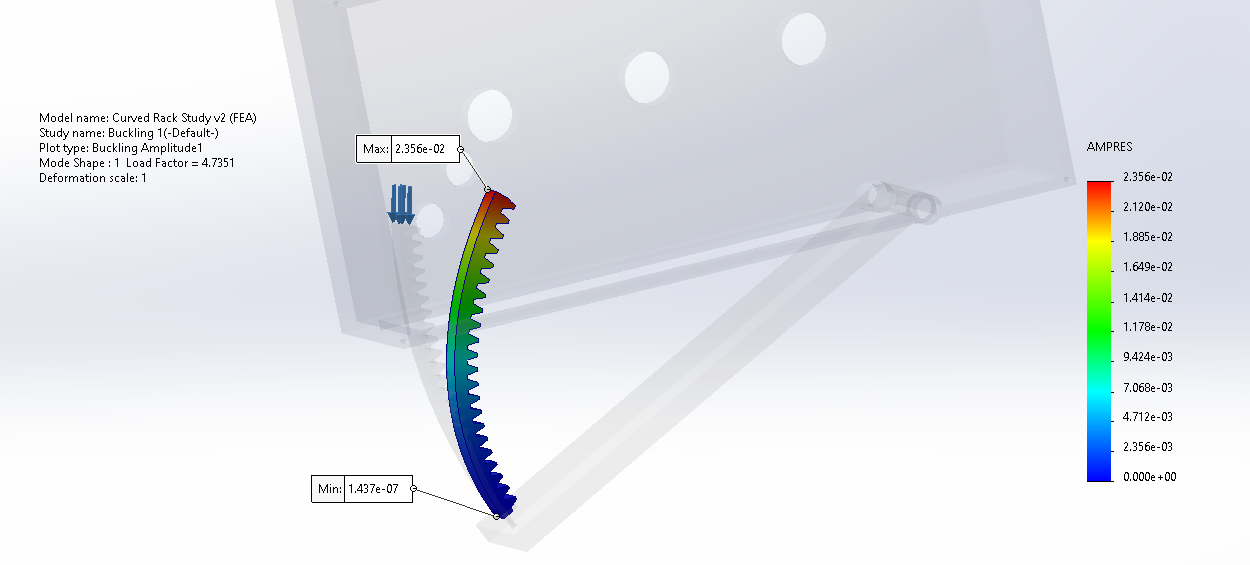
- Compared simplified-theory assumptions vs. curved-geometry FEA to bound stability margin.
-
Fatigue: Curved Gear Rack — FS = 1.09
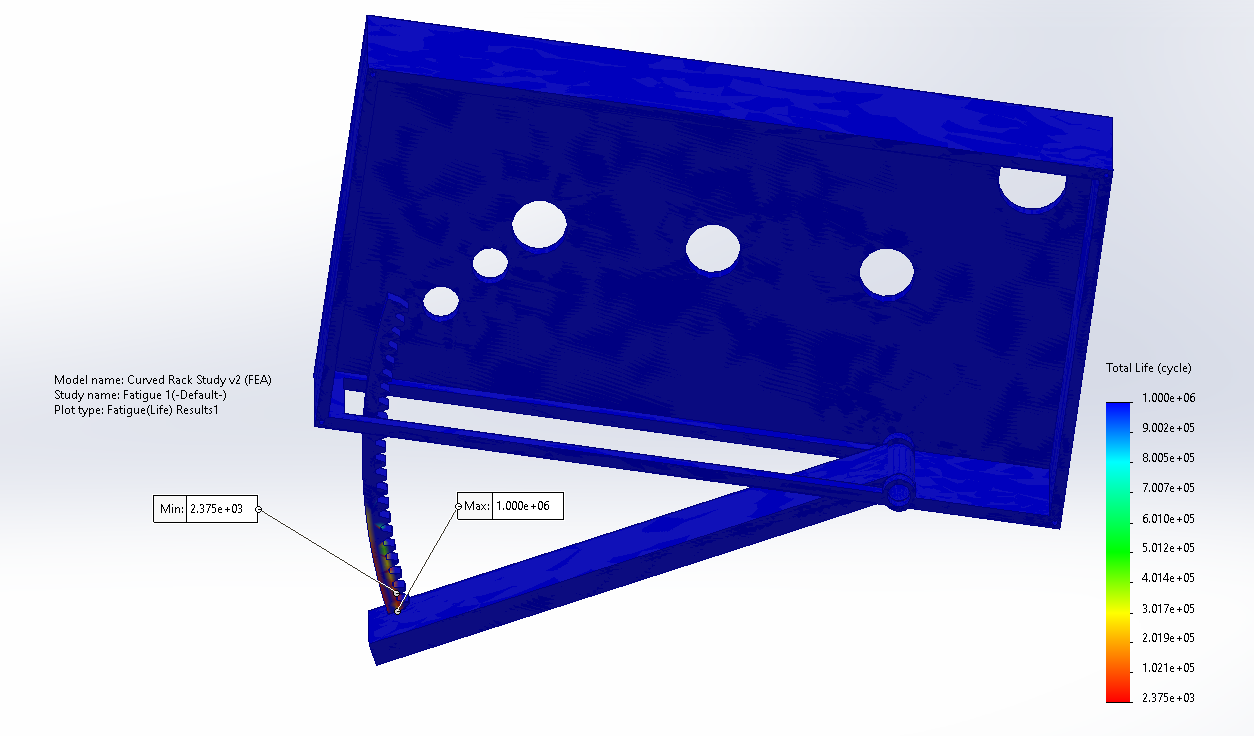
- Fatigue was a key driver; material selection was updated from Al 3003 to Al 5052 to improve factor of safety margin under cyclic squeezing.
-
Static: Curved Gear Rack — FS = 1.65
-
Connection